In the realm of sports, artistic gymnastics stands as a testament to human agility, artistry, and athleticism. From its humble origins to its captivating presence in the Olympics, this discipline has captivated audiences worldwide, showcasing the extraordinary abilities of its practitioners.
Artistic gymnastics encompasses a diverse range of disciplines, each demanding unique skills and techniques. From the graceful elegance of the uneven bars to the explosive power of the vault, gymnasts push the boundaries of human movement, defying gravity and inspiring awe.
Artistic Gymnastics Overview
Artistic gymnastics is a sport that combines strength, flexibility, and coordination. It is performed on various apparatuses, including the uneven bars, balance beam, vault, and floor exercise. Artistic gymnastics is a popular sport at the Olympic Games and is also enjoyed by people of all ages as a recreational activity.
The history of artistic gymnastics can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was part of the Olympic Games. The sport was later developed in Europe in the 19th century and became an official Olympic sport in 1896.
Disciplines within Artistic Gymnastics
- Men’s Artistic Gymnastics: Consists of six events – floor exercise, pommel horse, still rings, vault, parallel bars, and high bar.
- Women’s Artistic Gymnastics: Includes four events – vault, uneven bars, balance beam, and floor exercise.
Famous Artistic Gymnasts
- Simone Biles (USA): Widely regarded as the greatest gymnast of all time, with 32 Olympic and World Championship medals.
- Nadia Comaneci (Romania): The first gymnast to score a perfect 10 at the Olympics, in 1976.
- Li Ning (China): Won six medals at the 1984 Olympics, including three golds.
Gymnastics Equipment: Artistic Gymnastics
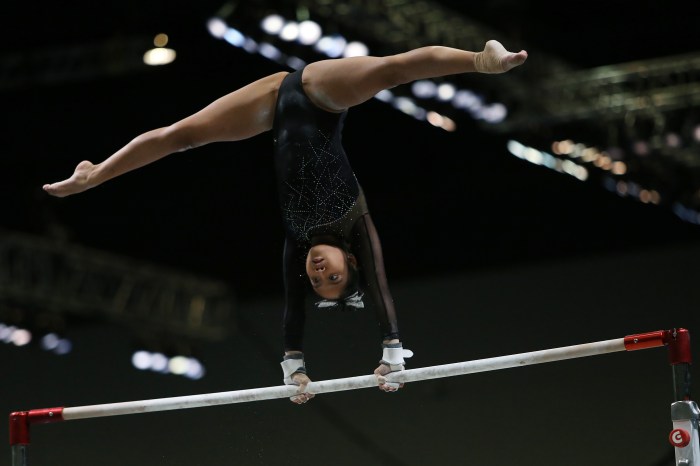
Apparatuses Used in Artistic Gymnastics
- Uneven Bars: Two horizontal bars set at different heights, used for swinging, circling, and release moves.
- Balance Beam: A narrow, elevated beam used for acrobatic and dance elements.
- Vault: A springboard used for powerful takeoffs into flips and twists.
- Floor Exercise: A large mat area where gymnasts perform tumbling, leaps, and dance routines.
Safety Precautions
- Proper warm-up and stretching to prevent injuries.
- Use of safety mats and spotters to minimize the risk of falls.
- Regular equipment maintenance and inspections.
Technology in Gymnastics Equipment
- Spring-loaded floors to enhance power and reduce impact.
- Electronic scoring systems for accurate and efficient judging.
- Motion capture technology to analyze and improve technique.
Training and Techniques
Training Methods
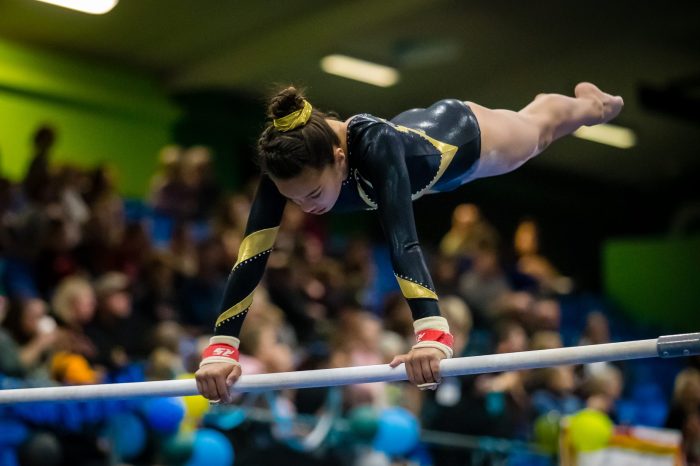
- Progressive overload: Gradually increasing training intensity and complexity.
- Specificity: Focusing on exercises that mimic competition movements.
- Periodization: Dividing training into phases with varying goals and intensity.
Importance of Flexibility, Strength, and Coordination
- Flexibility: Enables gymnasts to perform complex maneuvers and reduce risk of injuries.
- Strength: Essential for executing powerful and controlled movements.
- Coordination: Allows gymnasts to move smoothly and efficiently, combining strength and flexibility.
Common Gymnastics Techniques
- Handstands: Holding the body upside down, supported by the hands.
- Cartwheels: A continuous roll from hands to feet.
- Backflips: A backward somersault.
Competitions and Judging
Levels of Gymnastics Competitions
- Local and regional competitions
- National championships
- International competitions (e.g., World Championships, Olympics)
Scoring System
- Difficulty score: Based on the complexity of the routine.
- Execution score: Evaluates the precision and control of the performance.
Role of Judges
- Assess the difficulty and execution of each routine.
- Provide feedback and guidance to gymnasts.
- Ensure fairness and consistency in scoring.
Health and Safety in Gymnastics
Common Injuries
- Muscle strains and tears
- Joint sprains and dislocations
- Stress fractures
Importance of Proper Nutrition and Rest
- Provides energy and nutrients for intense training.
- Supports muscle recovery and reduces risk of injuries.
- Promotes overall well-being and performance.
Preventing Injuries
- Proper warm-up and stretching
- Gradual progression in training intensity
- Use of proper technique and equipment
Gymnastics as an Art Form
Artistic Elements of Gymnastics
- Choreography: The sequence of movements and skills performed.
- Music: Accompanies the routine and enhances its expressiveness.
- Body Lines: The graceful and controlled movements of the body.
Role of Choreography and Music
- Enhances the aesthetic appeal of the routine.
- Conveys emotion and expression through movement.
- Synchronizes the gymnast’s movements with the music.
Gymnasts Known for Their Artistry
- Svetlana Khorkina (Russia): Known for her elegant and powerful performances.
- Nastia Liukin (USA): Olympic all-around champion known for her graceful and expressive routines.
- Kohei Uchimura (Japan): Multiple Olympic and World champion known for his innovative and artistic floor exercises.
Gymnastics in the Olympics
History in the Olympics
- Gymnastics has been part of the Olympic Games since the first modern Olympics in 1896.
- Women’s gymnastics was added to the Olympics in 1928.
Events Included in Olympic Gymnastics
- Men’s: Floor exercise, pommel horse, still rings, vault, parallel bars, high bar, and team all-around.
- Women’s: Vault, uneven bars, balance beam, floor exercise, and team all-around.
Famous Olympic Gymnasts
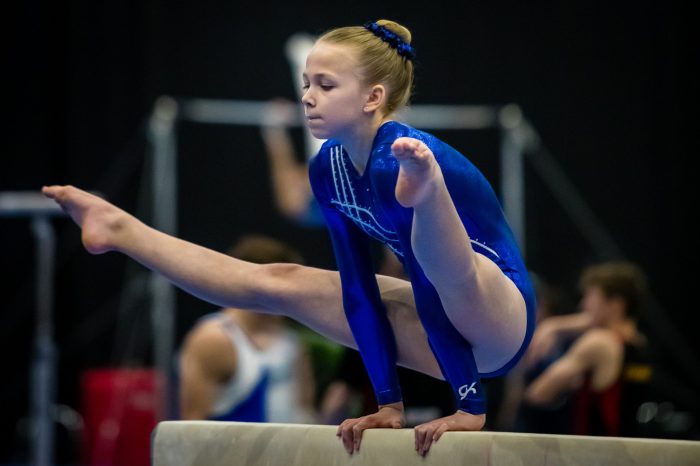

- Larisa Latynina (Soviet Union): Won 14 Olympic medals, including 9 golds.
- Nadia Comaneci (Romania): The first gymnast to score a perfect 10 at the Olympics, in 1976.
- Michael Phelps (USA): The most decorated Olympian in history, with 28 medals, including 23 golds.
Gymnastics for All
Benefits of Gymnastics, Artistic gymnastics
- Improved flexibility, strength, and coordination
- Enhanced self-confidence and discipline
- Reduced risk of obesity and chronic diseases
Getting Involved in Gymnastics
- Join a local gymnastics club or gym.
- Attend classes or workshops for beginners.
- Practice at home with basic exercises.
Resources for Gymnastics Classes and Programs
- USA Gymnastics: www.usagym.org
- International Gymnastics Federation: www.gymnastics.sport
Final Thoughts
Whether witnessed in the hallowed halls of Olympic arenas or in the dedicated training facilities where gymnasts hone their craft, artistic gymnastics continues to captivate and inspire. It is a testament to the human spirit’s capacity for excellence, where artistry and athleticism intertwine to create a breathtaking spectacle.
FAQ Explained
What are the different disciplines within artistic gymnastics?
Artistic gymnastics includes disciplines such as floor exercise, vault, uneven bars, balance beam, and horizontal bar for men.
What is the scoring system used in artistic gymnastics?
Gymnasts are scored based on the difficulty of their routines, execution, and artistry, with deductions for errors.
What are some common injuries associated with artistic gymnastics?
Gymnasts may experience injuries such as sprains, strains, fractures, and overuse injuries due to the demanding nature of the sport.