With how many neurons are in the human brain at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling liputan6 author style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
The human brain is an intricate organ composed of billions of neurons, the fundamental units of information processing. Understanding the number of neurons in the human brain is crucial for comprehending its complexity and function.
Neural Composition of the Human Brain
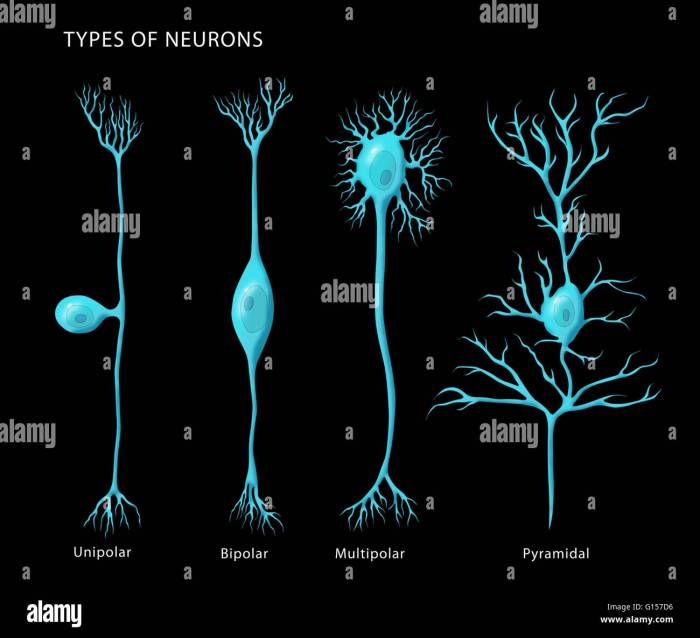
The human brain is composed of billions of neurons, the basic units of the nervous system. Neurons are specialized cells that transmit information throughout the body, enabling us to think, feel, and act.
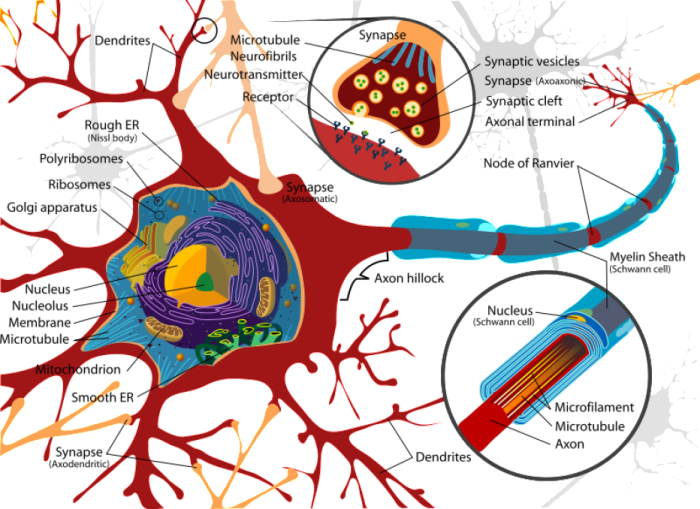
Basic Structure of a Neuron
A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles responsible for the neuron’s metabolic functions. Dendrites are short, branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons. The axon is a long, slender extension that transmits signals away from the cell body.
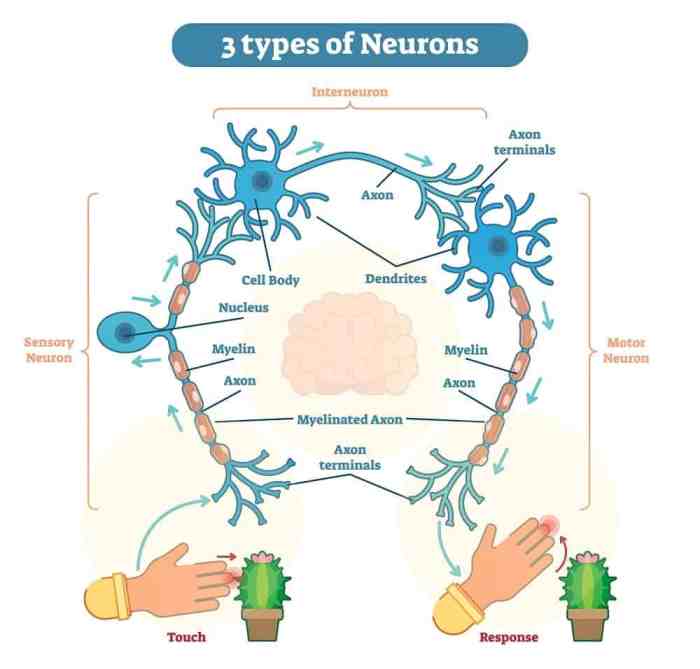
Types of Neurons
There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons transmit information from the body’s sensory receptors to the brain. Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
Organization of Neurons
Neurons are organized into complex networks within the brain. These networks are responsible for a wide range of functions, including perception, movement, memory, and emotion. The brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right hemispheres, which are connected by a thick band of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum.
Each hemisphere is further divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Different brain regions are responsible for different functions. For example, the frontal lobe is involved in higher-order cognitive functions such as planning and decision-making, while the occipital lobe is responsible for processing visual information.
Regional Distribution of Neurons
The human brain is a complex organ composed of billions of neurons, each with its own unique function. The number of neurons in different brain regions varies widely, reflecting the diverse roles these regions play in our cognitive and behavioral processes.
Estimated Number of Neurons in Different Brain Regions
The following table provides an estimate of the number of neurons in different brain regions:
| Brain Region | Estimated Number of Neurons |
|---|---|
| Cerebral Cortex | 14-16 billion |
| Cerebellum | 69 billion |
| Basal Ganglia | 70 million |
| Thalamus | 30 million |
| Hypothalamus | 2 million |
| Brainstem | 10 million |
Functional Significance of Regional Distribution
The regional distribution of neurons is not arbitrary. Rather, it reflects the specialized functions of different brain regions. For example, the cerebral cortex, which is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as language, memory, and reasoning, contains the highest number of neurons.
The cerebellum, which plays a crucial role in motor coordination and balance, has the second-highest number of neurons.
Variability in Regional Neuron Counts
The number of neurons in different brain regions can vary across individuals and species. For example, studies have shown that individuals with larger brains tend to have more neurons than those with smaller brains. Additionally, the number of neurons in certain brain regions, such as the hippocampus, has been found to decrease with age.
These variations may contribute to individual differences in cognitive abilities and susceptibility to neurodegenerative diseases.
Factors Influencing Neuron Count
The number of neurons in the human brain is not fixed but can vary based on several factors. These factors include genetics, environment, and experience, which can influence neural development and contribute to changes in neuron count.
Genetics
Genetic factors play a significant role in determining the number of neurons in the brain. Genes influence the production of proteins essential for neuron development, such as neurotrophic factors that promote neuron survival and growth.
Environment
Environmental factors, including nutrition, exposure to toxins, and physical activity, can also impact neuron count. Adequate nutrition is crucial for brain development, as nutrients provide the building blocks for neuron growth and function. Exposure to certain toxins, such as lead, can have neurotoxic effects and lead to neuron loss.
Experience
Experiences, such as learning and social interactions, can shape neural development and influence neuron count. New experiences can stimulate neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons, particularly in brain regions involved in learning and memory.
Neuron Loss and Neurogenesis
Changes in neuron count can also result from neuron loss and neurogenesis. Neuron loss occurs naturally as we age, particularly in certain brain regions, but it can also be accelerated by factors such as neurodegenerative diseases or trauma.
Neurogenesis, the birth of new neurons, is an ongoing process in specific brain regions, such as the hippocampus. Neurogenesis contributes to brain plasticity and the ability to learn and adapt to new experiences.
Comparison to Other Species
The human brain stands out for its complexity and cognitive abilities, and a key factor in this is the sheer number of neurons it contains. However, how does the human brain compare to other species in terms of neuron count?
To provide a comprehensive perspective, we have compiled a table comparing the estimated number of neurons in the brains of various animals:
| Species | Number of Neurons |
|---|---|
| Human | 86 billion |
| Elephant | 257 billion |
| Bottlenose Dolphin | 33 billion |
| Chimpanzee | 39 billion |
| Dog | 530 million |
| Mouse | 75 million |
As the table shows, the human brain has a significantly higher number of neurons compared to most other species. Even animals with larger brain sizes, such as elephants, have a lower neuron count than humans.
The evolutionary implications of these differences are intriguing. The high neuron count in the human brain is thought to have contributed to our advanced cognitive abilities, including language, reasoning, and problem-solving. It suggests that the increase in neuron count over the course of human evolution has been a key factor in our species’ success.
Interestingly, there is not a direct correlation between brain size and neuron count. For example, elephants have larger brains than humans but fewer neurons. This suggests that the number of neurons is a more important factor in determining cognitive abilities than brain size alone.
Clinical Significance
Changes in neuron count can significantly impact brain function and health. A reduction in neuron count can lead to cognitive decline, memory loss, and impaired motor function. Conversely, an increase in neuron count has been associated with improved learning and memory.
Neuron Loss in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons. This neuron loss leads to a decline in cognitive function and motor skills. In Alzheimer’s disease, the loss of neurons in the hippocampus, a brain region involved in memory, is associated with memory loss and cognitive decline.
Neuron Regeneration in Brain Repair and Recovery, How many neurons are in the human brain
The ability of the brain to regenerate neurons is limited, but research suggests that it may be possible to stimulate neuron regeneration to repair brain damage and restore function. For example, studies have shown that exercise can promote neuron regeneration in the hippocampus, which may have implications for treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Final Review
In conclusion, the number of neurons in the human brain is a testament to its extraordinary complexity and adaptability. Ongoing research continues to unravel the mysteries surrounding these essential cells, promising advancements in our understanding of brain function and potential treatments for neurological disorders.
FAQ Summary: How Many Neurons Are In The Human Brain
How many neurons are in the human brain?
The estimated number of neurons in the human brain ranges from 86 billion to 100 billion.
What factors can affect the number of neurons in the brain?
Genetics, environment, experience, neuron loss, and neurogenesis all play a role in shaping neural development and neuron count.
How does the number of neurons in the human brain compare to other animals?
Humans have a significantly higher number of neurons compared to other animals, contributing to our advanced cognitive abilities.